High forage protein intake positive for muscle recovery after exercise
Sara Muhonen, AgrD
Early harvested forage has high energy content but also often high crude protein content and it seems that how much protein the diet provides and the protein source affects the muscle glycogen storage. In this study 6 trotters in training were fed two diets that consisted of early harvested grass silage with high energy content (> 11 MJ ME/kg DM). One silage had high crude protein content (16.6%) that gave an excess protein intake and the other silage (12.5%) provided a recommended intake of crude protein. The horses were fed only the forages supplemented with minerals and salt. Three horses started on the high protein diet and three on the recommended protein diet and then they switched so all horses were tested on both diets. The horses were fed the diets for 3 weeks before exercise tests on a treadmill were performed.
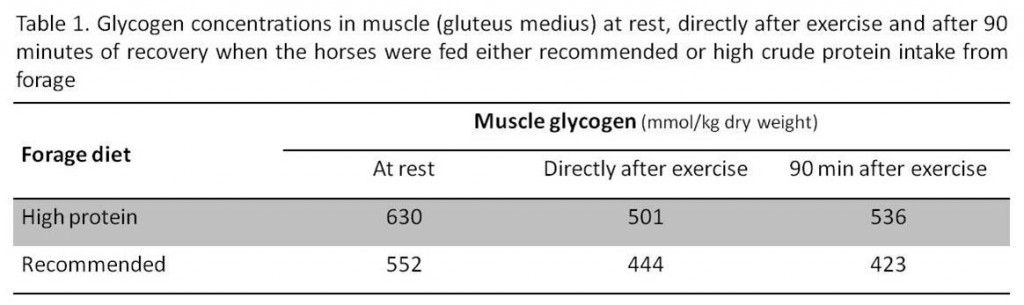
Before, during and after the exercise tests no significant differences could be detected in heart rate, breathing frequency, plasma lactate and blood pH. When the horses were fed the high protein forage they had higher concentrations of muscle glycogen at rest, directly after exercise and after 90 minutes of recovery after exercise (Table 1). Directly after exercise the concentrations of muscle glycogen were lower on both diets. When the horses were fed the forage providing recommended crude protein intake the muscle glycogen was still low 90 minutes after exercise whilst when the horses were fed the high protein forage the muscle glycogen tended to increase already 90 minutes after exercise. This indicates a more rapid glycogen synthesis when the horses were fed the high protein forage.
Also the muscle concentration of the amino acid leucine was higher at rest, directly after exercise and 90 minutes after exercise when the horses were fed the high protein forage. Other studies have shown that an increased muscle concentration of amino acids such as leucine is beneficial for muscle recovery after exercise.
In conclusion this study has shown that high crude protein intake from forage increases the muscle concentration of glycogen and the amino acid leucine in Standardbred trotters in training, which can be beneficial for muscle recovery after intensive exercise.
Reference:
Essén-Gustavsson B, Connysson M & Jansson A. 2010. Effects of crude protein intake from forage-only diets on muscle amino acids and glycogen levels in horses in training. Equine Veterinary Journal 42 (Suppl. 38), 341-346.